Project Charter Template
Stay within scope, focus on deliverables, and get your entire team on the same page using a Project Charter Template.
About the Project Charter Template
Before diving into a project, it's important to make sure you have the necessary documentation that will help you succeed. One key document that you need is a project charter.
Read on to learn more about what a project charter is, when you should use one, and how you can create one using our Project Charter Template.
What is a project charter in project management?
A project charter is a unified source of truth for the details of a project. A project manager or project leader relies on the project charter to explain the core objectives, scope, and responsibilities of a project and its team, as well as some other key details. No matter how wide the project’s scope, the project manager can always refer back to the charter if anything is ever uncertain.
From the moment your project kicks off, a charter can help align every stakeholder around a shared understanding of the project’s objectives, strategies, and deliverables.
Ideally, the project sponsor, who is accountable for the project’s successful delivery, should write the project charter document. In reality, this task often falls to the project manager to draft before it is signed off by senior stakeholders or the project board.
When should you use a project charter?
When you’ve already got a budget, a project plan, a project schedule, and a statement of purpose, why do you need a project charter?
A project charter serves as a single source of truth that supersedes all others — you could call it the founding scripture of your project. When conflicts arise between the budget and timeline or between members of the team, the project leader can use the charter to arbitrate.
The more complex a project gets, and the more stakeholders and moving parts it acquires, the harder it becomes for the project manager to keep everyone on task without a project charter.
Charters are also crucial when you need to sell your project to key stakeholders — especially to decision-makers who may lack the technical knowledge of your project team. The charter is an elevator pitch that makes it easy for gatekeepers to understand the project details.
How to create a project charter
Do you want the easiest way to build a project charter that works the first time? Work from a template. Start by adding the Project Charter Template to your Miro board. Then, follow these steps:
Invite your project team members. The more people can contribute their input to the charter, the more smoothly you can work together on the project itself. Invite everyone to collaborate on your Miro workspace.
Brainstorm answers to the key categories. Below these steps, you’ll find a rundown of all the key sections in the template.
Fill in the results. Once you and your collaborators have settled on what information should go in each category, fill them in on the template.
Use the charter to get buy-in. Shop the finished template around to each stakeholder and get their opinion. As you go, make any changes necessary.
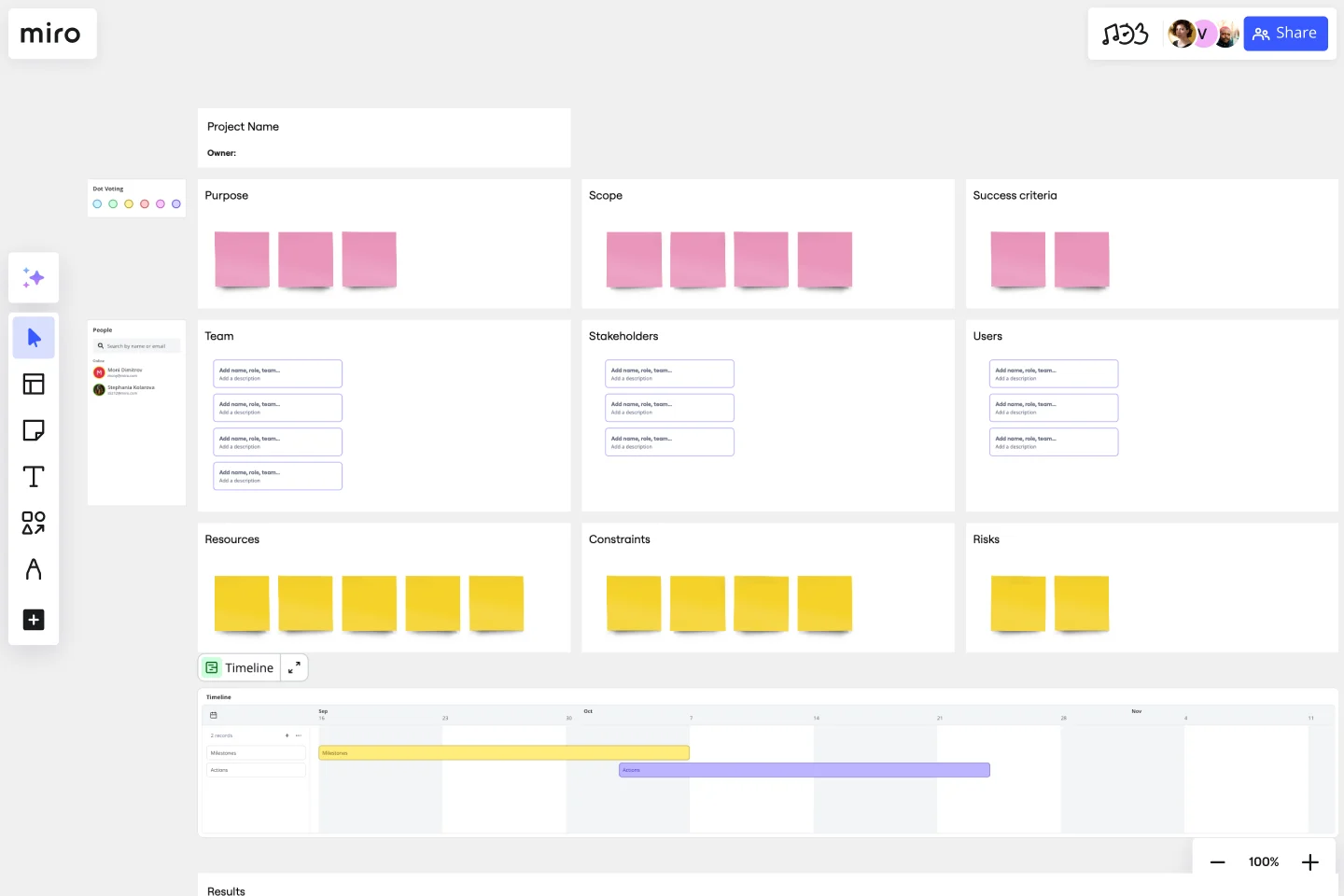
For a charter to be effective, it’s important for the project leader to include as many details as possible. At a minimum, you should make sure to address a few essential elements. The template includes 10 total sections.
Purpose is the ultimate goal of the project, the reason you’re launching it at all. Examples can include filling a niche, increasing customer loyalty, or boosting revenues.
Scope defines what is and isn’t part of the project. Define your scope clearly so your project doesn’t succumb to scope creep, continually bloating with new features and shipping far behind schedule.
Success criteria is a SMART goal (specific, measurable, actionable, relevant, and time-bound) that can tell you whether the project has succeeded. A project with a criterion of “delighting all our customers forever” is bound to fail. Instead, try something like “obtain the highest market share in our industry.”
Team lists the people who will work directly on the project.
Stakeholders are people who aren’t on the project team, but who have a specific reason to care about how it turns out.
Users are the people the project is intended to benefit (in a way that pays dividends to your company). Unlike “team” and “stakeholders,” users will be segments of the population instead of specific people.
Resources are the organizational assets you can devote to the project, including money, time, people, equipment, and more.
Constraints are known factors that may get in the way of the project succeeding.
Risks are events which may or may not occur, but would threaten the project’s success if they did happen.
Timeline is a rough sketch of how long the project will take to complete, including action items that will define each phase and projected dates for key milestones.
Don’t go overboard on any of these points. The finished project charter shouldn’t be longer than a few pages. All the key information it holds needs to be visible at a glance.
Discover more project charter template examples and simplify your planning.
What is the main purpose of a project charter?
A charter is the ultimate source of truth for any questions that arise during execution. Whenever there’s conflict or ambiguity between objectives, people, or teams, the project manager or project sponsor can refer to the charter to clear it up.
How do you build a project charter?
Start by getting your team together in a collaborative workspace like Miro. Adding sticky notes to the template is a simple way to build consensus on key points about the project. Each of the template’s ten sections corresponds to a vital part of a charter: purpose, scope, success criteria, team, stakeholders, users, resources, constraints, risks, and timeline.
What should a project charter include?
At the bare minimum, a charter should list the project’s objectives, scope, deliverables, high-level budget, and the responsibilities of each team member. There are several other elements that the project sponsor may wish to consider. For example, risk identification and mitigation plans, the project timeline, a list of expected resource requirements, a list of key project stakeholders, and a project communication plan.
Get started with this template right now.
Value Stream Mapping SAFe Template
Works best for:
Agile, Value Stream Mapping
The Value Stream Mapping SAFe Template in Miro is designed to help teams visualize and optimize their workflows within the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe). This template provides a structured approach to mapping out the current state of your value stream, identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and planning for a more efficient future state. By leveraging this template, teams can ensure that they are aligned with SAFe principles and continuously improving their processes.
AI Product Canvas
Works best for:
Product Management, Planning
The AI Product Canvas template facilitates the development of AI-powered products with a comprehensive framework. By defining AI capabilities, data requirements, and ethical considerations, this template guides teams through the AI product development process. With sections for identifying use cases, defining algorithms, and assessing model performance, it ensures that AI solutions meet user needs and ethical standards. This template serves as a strategic guide for developing innovative AI products that deliver value and drive business success.
Product Canvas Template
Works best for:
Desk Research, UX Design
Product canvases are a concise yet content-rich tool that conveys what your product is and how it is strategically positioned. Combining Agile and UX, a project canvas complements user stories with personas, storyboards, scenarios, design sketches, and other UX artefacts. Product canvases are useful because they help product managers define a prototype. Creating a product canvas is an important first step in deciding who potential users may be, the problem to be solved, basic product functionality, advanced functionalities worth exploring, competitive advantage, and customers’ potential gain from the product.
FMEA Analysis Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Strategic Planning, Software Development
When you’re building a business or running a team, risk comes with the territory. You can’t eliminate it. But you CAN identify it and mitigate it, to up your odds of success. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a powerful tool designed to help you manage risk and potential problems by spotting them within a process, product, or system. And you’ll spot them earlier in your process—to let you sidestep costly changes that arise late in the game or, worse, after they’ve impacted your customers and their experience.
Research Template
Works best for:
Education, Desk Research, Product Management
Teams often need to document findings from usability testing sessions and customer interviews into a systematic, flexible user research template. Collecting everyone’s observations into a centralized location makes it easier to share insights company-wide and suggest new features based on user needs. Research templates can be used to record quantitative or qualitative data.. When it’s your job to ask questions, take notes, learn more about your user, and test iteratively, a Research Template can help you validate your assumptions, find similarities across different users, and articulate their mental models, needs, and goals.
Service Blueprinting Workshop
Works best for:
Agile
The Service Blueprinting Workshop template helps teams visualize and improve service processes. It includes ice breakers, context canvas, empathy maps, and action plans for service transitions. Use it to align teams, identify opportunities, and prototype service delivery from a macro to microscopic level, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of service orchestration and seamless collaboration. Ideal for remote and dispersed teams.