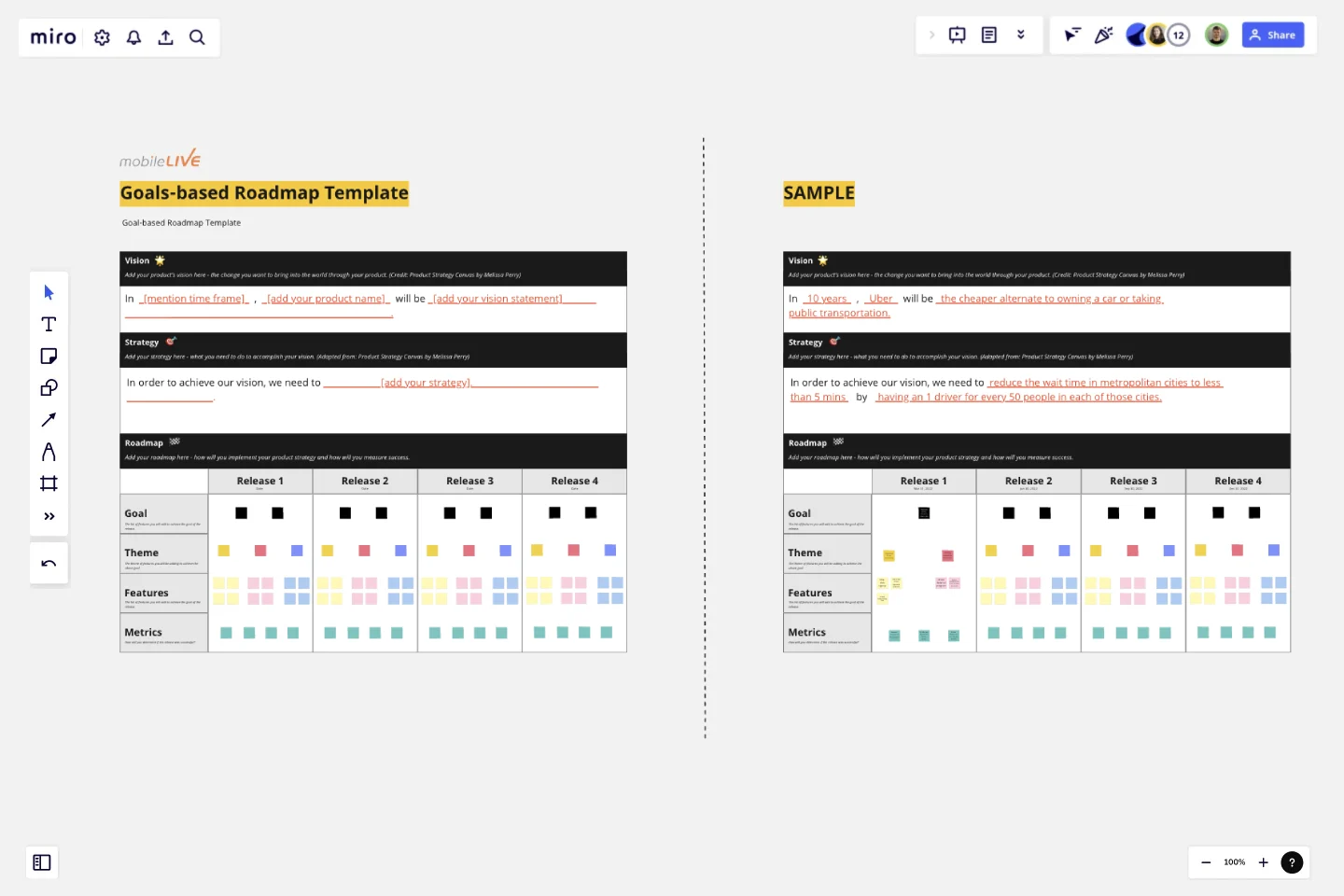
Goals-based Roadmap
Many companies keep rolling out roadmaps just for the sake of it. In most cases, these roadmaps turn the teams (and the organization) into incoherent feature-building factories with no goals, no strategy and no eye on contributing towards the organization’s long-term vision.
With feature-based roadmap templates, no matter how religiously you follow your strategy, it is only a matter of time before you succumb to the myriad feature requests that will be thrown at you from all directions; whether it be from a sales person coming from a client demo where the client was not willing to buy our product unless it supported an Active Directory integration, or directly from the C-level executive who spent the weekend trying out competitor products and came across a list of feature ideas to copy. Having lost sight of the bigger picture in order to appease the executives, your roadmap would soon turn into an incoherent feature factory, with very little alignment with the strategy.With feature-based roadmaps, roadmaps can also often become contractual obligations with the stakeholders, rather than a view of progress your product is expected to make towards achieving its strategic goals.
Goals-based Roadmaps
Goals-based roadmaps shift the focus of the team from shipping features to delivering value and achieving product goals. While the features are still part of the roadmap template, the focus is always on meeting Goals set for each release.
How to use Goals-based Roadmap board?
Before you start building your roadmap, it is imperative that you and your team fully understand and are aligned on the Product's Vision and Strategy. By having both the Product Vision and the Strategy as part of the Roadmap template can serve two purposes:
The teams understand that they can't miss this step before they start creating a roadmap.
During the monthly/quarterly roadmap review sessions, the Vision and Strategy sections can also serve as a referesher for the team.
Step 1: Fill in your product vision
In the first section, add your product's vision here, which is the change you want to bring into the world through your product. We have used the Vision format from the Product Strategy Canvas by Melissa Perry. Feel free to plug in anyother format you prefer.
Step 2: Fill in your product strategy
In the second section, add your product's strategy here, which is what you need to do to accomplish your vision. Here, we have adapted Melissa Perry's Product Strategy Canvas format.
Step 3: Set the Goals
When you get into the roadmap section, the first step is to set the goals you want to achieve as part of your Product Strategy. Breakdown the goals into a prioritized set of releases over a period of time. You can use this board to create a roadmap from 3 months to 3 years.Each release can have one or more goals. As a general rule, we don't recommend having more than 3 goals per release as that can end up diverting the team's focus.
Step 4: Identify the Themes
Once you have defined your goals, you need to identify the themes for your roadmap features that will allow you to achieve your goals. These themes will often come from your customer research exercises and will be directly linked with your goals.
Step 5: List down the metrics of success
For each release, you should identify the metrics that will determine whether your release was successful in meeting its goal or not. These metrics need to be high-level and should be independent of any features that will be shipped as part of each release.
Step 6: Review your Goals, Themes & Metrics
Before you move ahead, it is important to review your Goals & Themes with other stakeholders and get their buy-in.
Step 7: Add features (Not to be shared outside the product and development team)
With everything else jotted down, now is the time to think about the low-level details pertaining to identifying features that will help you in achieving your release goals.We have kept this item towards the end (and even after the stakeholders review) because in today’s day and age, premature convergence on a solution (in the form of features), way before time, is very risky. Including such low-level details into your roadmap leaves very little room for your team to innovate and improvise. In most cases, they feel less valued because they are being spoon-fed and are bound to lose motivation over time.
Final Step: Adapt
You can continue to adapt your roadmap on a regular basis based on new information received from your customers. In most cases, you would only need to change the list of features you put in as part of each release, with the Goals and themes requiring very minor updates.
Credits
Product Strategy Canvyas by Melissa Perry
The Go Roadmap template by Roman Pichler
This template was created by Sami Rehman.
Get started with this template right now.
Pros and Cons List Template
Works best for:
Decision Making, Documentation, Strategic Planning
A pros and cons list is a simple but powerful decision-making tool used to help understand both sides of an argument. Pros are listed as arguments in favor of making a particular decision or action. Cons are listed arguments against it. By creating a list that details both sides of the argument, it becomes easier to visualize the potential impact of your decision. To make your pros and cons list even more objective, it can help to weight each pro and con against the others. You can then present your decision with confidence, making a strong argument for why it’s the right one.
OKR Board for Product, UX and Engineering Teams
The OKR Board for Product, UX, and Engineering Teams template aligns cross-functional teams around common objectives using Objectives and Key Results (OKRs). By setting ambitious goals, defining measurable outcomes, and tracking progress collaboratively, this template fosters alignment and focus. With sections for defining team OKRs, prioritizing initiatives, and monitoring performance, it enables teams to work cohesively towards shared goals. This template serves as a catalyst for driving product innovation and delivering exceptional user experiences.
Fishbone Diagram for Marketing
Works best for:
Fishbone Diagram
Optimizing marketing strategies requires identifying underlying issues. The Fishbone Diagram Marketing template helps you systematically explore factors affecting your campaigns. Categorize potential causes into areas such as market research, product positioning, promotional strategies, and distribution channels. This structured analysis enables your team to pinpoint and address issues, enhancing marketing effectiveness and achieving better results.
Fishbone RCA
Works best for:
Problem solving, Strategy
Use the Fishbone RCA template to conduct a thorough root cause analysis (RCA) for any problem. This template helps you break down complex issues into manageable categories, enabling you to identify the underlying causes. It's an effective tool for improving processes, solving problems, and preventing future issues.
Product Strategy - Understand the "Why"
Works best for:
Product Management, Planning
The Product Strategy Understand the Why template emphasizes the importance of aligning product strategies with business objectives. By defining the "why" behind product initiatives, setting clear goals, and prioritizing initiatives, this template ensures strategic alignment and focus. With sections for articulating vision, setting objectives, and defining success criteria, it provides clarity and direction for product teams. This template serves as a strategic guide for product managers to develop and execute product strategies that drive business growth and customer value.
Customer Journey Map by Hustle Badger
Works best for:
Customer Journey Map
Customer journey mapping is a method that visualizes and narrates how users navigate a site or app to achieve their objectives.