Fibonacci Scale Template
Estimate how much effort it takes to perform tasks and assign teams during a work sprint efficiently with the Fibonacci Scale Template.
About the Fibonacci Scale Template
The Fibonacci scale is a series of numbers based on the Fibonacci sequence (0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, etc.). In the context of Agile, these numbers are used to estimate and agree upon the amount of effort required to complete a specific task. At the beginning of an Agile sprint, a team will discuss the various tasks that need to be completed and assign points to each task based on the Fibonacci scale.
What is the Fibonacci scale?
The Fibonacci sequence contains numbers that exhibit exponential growth, where each number is the sum of the two previous ones. That’s why Agile teams have come to use the Fibonacci scale for business because it’s easier to evaluate task efforts when you don’t have many numbers close to each other to choose from, as opposed to an even scoring scale. When managing a team, it’s often important to estimate how long it might take to complete a given task. More complex tasks are assigned more points, and smaller tasks are assigned fewer points. Managers can then review and prioritize tasks depending on their points. The Fibonacci scale is used to assign those point values.
How does the Fibonacci scale work?
The numbers in the Fibonacci scale are based on the Fibonacci sequence. In this sequence of numbers, each number is the summation of the two previous numbers. In the context of Scrum, the numbers represent the level of complexity and degree of difficulty involved in completing a task. For example, a task assigned “0” points would be very simple and quick to complete, a task assigned “1” point would be slightly more complex or time-consuming, and so on and so forth. Since the Scrum approach generally works in one-week sprints, it’s unlikely that many tasks will be assigned “21.”
Why use the Fibonacci scale?
The Fibonacci scale is a useful tool for a variety of reasons. For one, its growth is exponential. When estimating how long it might take to complete a task, estimating time for shorter tasks is much easier than estimating time for longer tasks. An exponential scale reflects that growing uncertainty. As you move up the scale, the numbers quickly become much larger.
Relatedly, the Fibonacci scale forces your team to make a choice. For example, when estimating time for a complex task, you ask, “is it an 8, 13, or 21?” and there is no in-between. This intuitive anchoring mechanism cuts down on debate and helps you make clear judgment calls.
Overall, the Fibonacci scale is a powerful method to ensure that work is distributed evenly and can help ensure that everyone is accurate when estimating the work and time involved in a project. If your team uses this approach on an ongoing basis, you will likely become more accurate and avoid overcommitting during each sprint.
How to use the Fibonacci Scale Template in Miro
Start selecting our ready-made Fibonacci Scale Template. It will help you visualize your team’s tasks, evaluate efforts and prioritize them.
The Fibonacci Scale Template is divided into three sections:
User stories
Here is where you list tasks or user stories you want to estimate. If you use Jira, import stories as cards directly with the Jira app. Afterward, discuss with your team the risk and effort for each story.
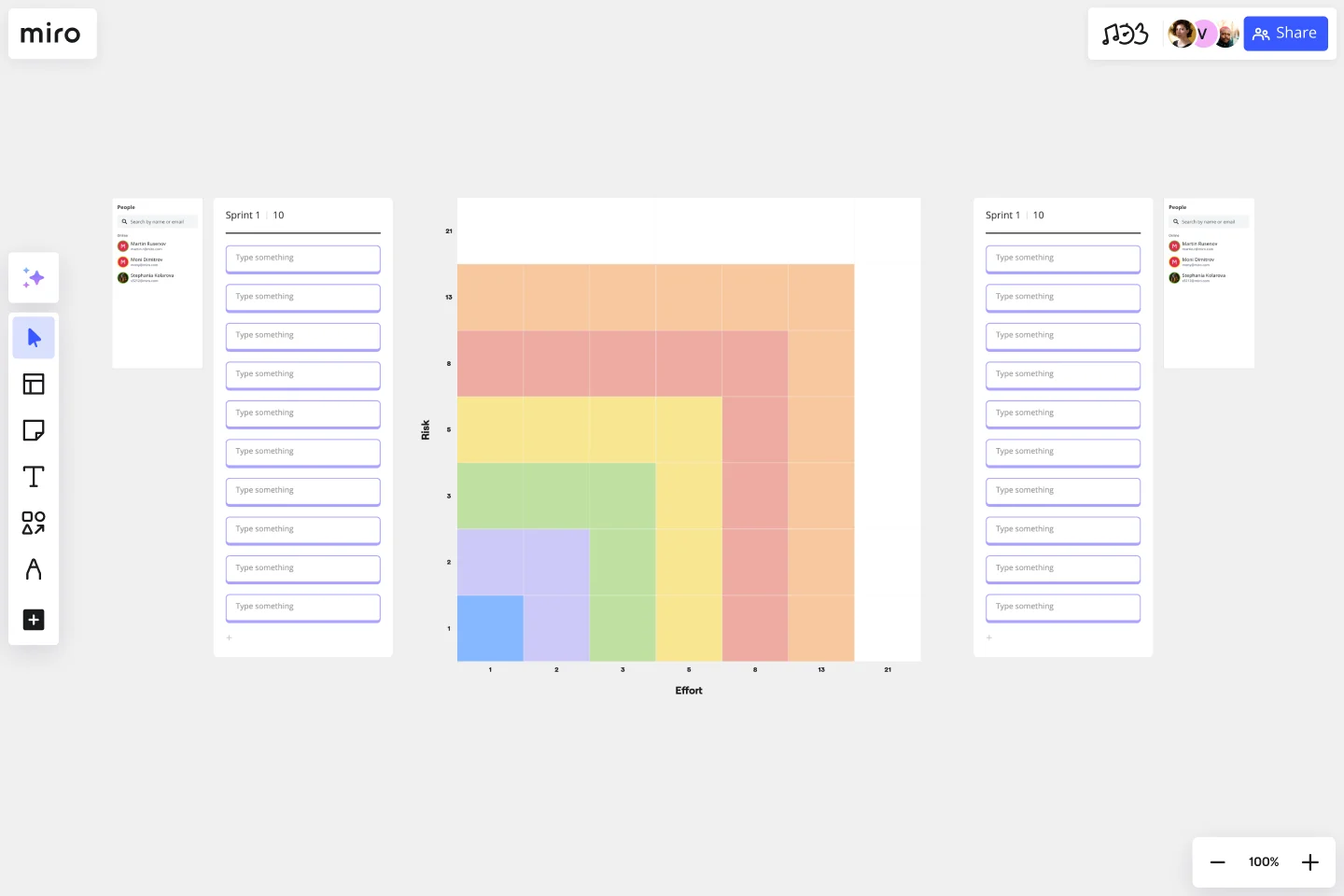
Fibonacci Scale
Place the stories previously added to the sprint onto the Fibonacci scale matrix. Following your discussion, add them to the appropriate region according to their effort and risk levels.
To get perspectives and assess correctly how much effort and risk a task might take, allow each member to vote on the tasks with a unique emoji or sticker.
Priorities
Based on the Fibonacci scores and the team's prioritization, copy or drag stories onto the priorities frame. Be mindful of your team's capacity, and prioritize taking everyone’s opinions and schedules into consideration.
If you’re finding it hard to estimate task points, Artem Shein, Agile coordinator, created an interesting and fun template to help you and your team give points to tasks. Try it out!
Example of the Fibonacci Scale Template in action
Let’s say you are launching different product functionalities. You have user stories that look like this:
Service catalog
Calendar integration
Video integrations
Live cursors
After everyone has added their tasks to the Fibonacci scale, these are the points each task has:
Calendar integration: 8
Live cursors: 5
Video integration: 3
Service catalog: 2
To prioritize this list, start with the tasks with the least effort and lower risk. Those are the ones that your team will be able to deliver quicker. Afterward, list the ones that range from medium to high effort.
If you think a task that is higher up on the scale might not require so much effort, discuss it with your team to see what you can do to make its completion easier. You can also use Miro's Planning Poker tool to do better estimations with your team.
Create your priority list according to your team’s feedback and assign each task to its owner via Jira cards or tagging the stickies on your Fibonacci Scale Template.
Get started with this template right now.
Retrospective in the Island of Golocans
Works best for:
Retrospectives, Meetings, Agile Methodology
The Retrospective in the Island of Golocans template offers a creative and imaginative setting for retrospectives, transporting participants to a fictional island setting. It provides elements for reflecting on past iterations, sharing insights, and brainstorming improvements. This template enables teams to step outside their usual environment and approach retrospectives with a fresh perspective. By promoting creativity and storytelling, the Retrospective in the Island of Golocans empowers teams to engage in meaningful discussions, generate new ideas, and foster a culture of innovation effectively.
3x3 Prioritization Method Template
Works best for:
Operations, Prioritization, Strategic Planning
It’s all about assessing a task or idea, and quickly deciding the effort it will take and the potential impact it will have—ranked low, medium, or high. That’s what the 3x3 prioritization method does: Help teams prioritize and identify quick wins, big projects, filler tasks, or time-wasters. With nine bucket areas, it offers slightly greater detail than the 2x2 Prioritization Matrix (or Lean Prioritization Method). It’s easy to make your own 3x3 prioritization matrix—then use it to determine what activities or ideas to focus on with your valuable resources.
Affinity Diagram Template
Works best for:
Desk Research, Mapping, Product Management
You can use an affinity diagram to generate, organize, and consolidate information that comes out of a brainstorming session. Whether you’re building a product, working through a complex problem, establishing a process, or piecing apart an issue, an affinity diagram is a useful and simple framework that gives each team member the opportunity to pitch in and share their thoughts. But it’s not just ideal for brainstorms—this is a great template and tool when you need to reach consensus or analyze data such as survey results.
Agile Transition Plan Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Agile Workflows
An Agile transformation roadmap can help you, your team, and your organization transition from rigid compliance-heavy methods to the more flexible Agile way of doing things incrementally. From requirements to integrations to security, you can map out your organization's moving parts as “swim lanes” that you can then update regularly. Use your roadmap as a way to tell the story of how you see your product growing over a period of time. Get buy-in without overselling and keep your roadmap simple, viable and measurable. By using an Agile transformation roadmap, you can avoid getting bogged down in details and instead invest in big-picture strategic thinking.
Easter Egg Retrospective
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Retrospectives, Meetings
The Easter Egg Retrospective template offers a themed approach to retrospectives, incorporating elements of the Easter holiday. It provides elements for reflecting on past iterations, hunting for hidden insights, and brainstorming improvements. This template enables teams to have fun while addressing serious topics, fostering creativity and collaboration. By promoting a playful yet productive atmosphere, the Easter Egg Retrospective empowers teams to uncover hidden gems, drive improvement, and strengthen team cohesion effectively.
Impact/Effort Matrix Template
Works best for:
Project Management, Strategic Planning, Prioritization
Growing organizations have countless to-do’s and only so many hours in a day (or weeks before a big launch) to get them done. That’s where an impact effort matrix comes in. It gives you a quick visual guide to help prioritize your tasks and know exactly what’s worth doing. Using our template, you can create a matrix that organizes your activities into four main categories: quick wins that are low effort, effort-intensive projects that provide long-term returns, fill-ins that are low effort but low value, and time-wasters.