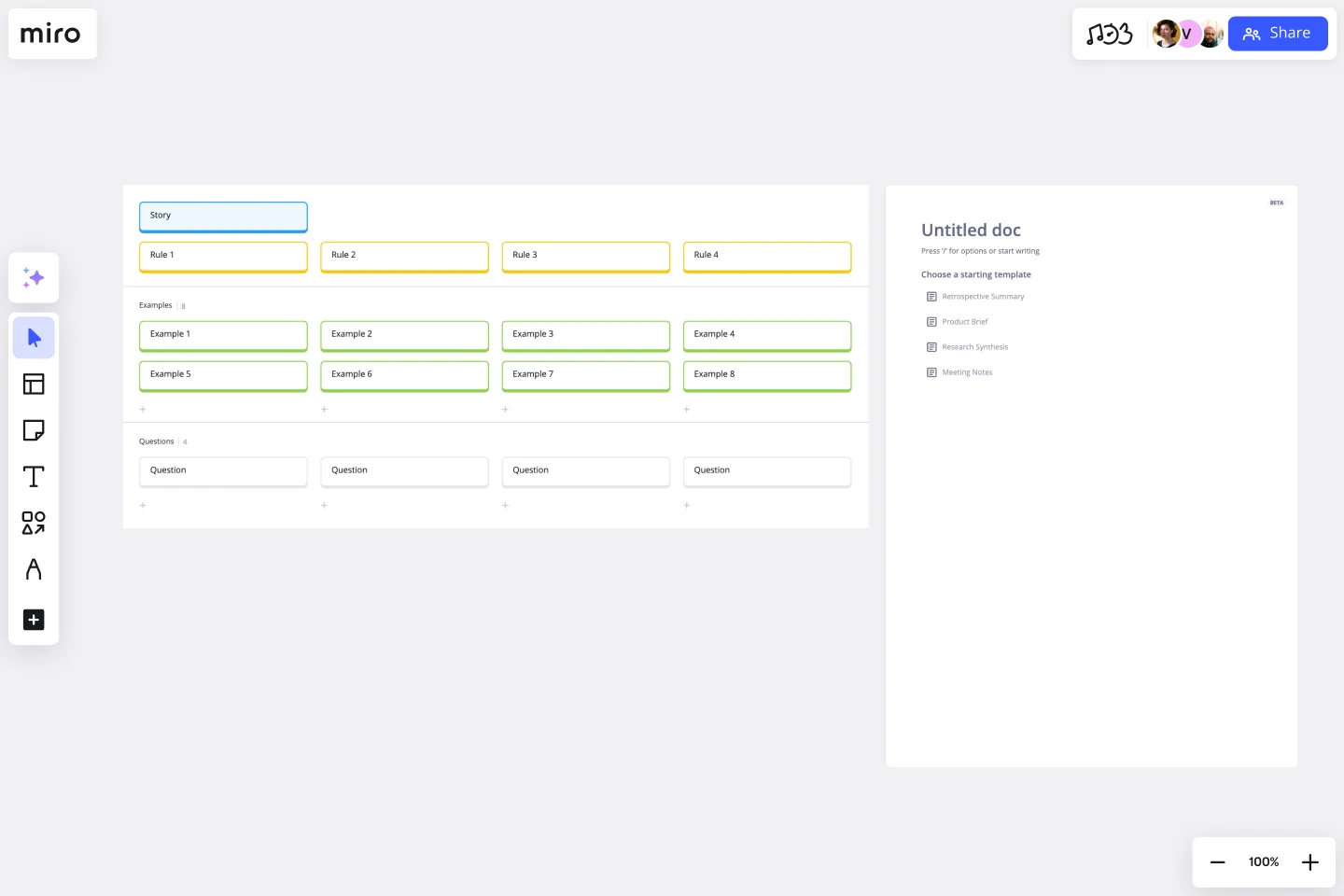
Example Mapping Template
Create a shared understanding of a new product feature.
About the Example Mapping Template
Example mapping (or user story mapping) helps product managers and their teams quickly break down product backlogs. Ideally, example maps help a cross-functional team (for instance, a product owner, tester, and developer) build up a shared understanding and language for why product features need to be added or changed.
Team leads can offer strategic direction toward a cohesive digital transformation (or timely upgrade) so your team has the relevant technology to stay competitive.
What is example mapping?
An example mapping session is a great way to develop structured, concrete user stories. Each example uncovered can help teams explore problem areas for customers and decide on acceptable criteria to build a new feature.
There are a few key elements that an example mapping tool can delineate:
Rules that sum up examples or agree on the scope of the user story
Questions or assumptions about situations where no one knows the ideal outcome
New stories that should be discovered or left out of the final scope
Example mapping also relies on a color-coded system to shape the scope of a user story:
Yellow sticky notes are for defining stories, such as “change of delivery address”
Blue sticky notes are for defining rules, such as “ETA is updated”
Green sticky notes are for defining examples, like “New address is out of range”
Red sticky notes are for questions, like “what if the customer lives outside the free shipping zone?”
This color-coded system helps steer the conversation in the right direction and keep the discussion on track. You can use a blank example mapping template to quickly and easily begin filling in the relevant fields to get the conversation started.
When to use example mapping
Example mapping is a collaborative method that can help your team define what accepted user behavior looks like for different scenarios. An example mapping tool can be a useful way to align your cross-functional teams toward:
Empathy for the customer and the team. Everyone should understand why new product features are needed, and what the customer may be struggling with as far as conflicts between stories and rules.
Shared understanding of the industry or product. By the end of the example mapping session, the team should leave with a shared language and appreciation for what’s at stake.
Small yet impactful potential for change. Think big and act small as a team. How soon can each recorded user story be translated into a real feature?
Rules and examples that follow logic. Specific rules and scenarios should back up every user story.
Create your own example map
Making your own example map is easy with Miro's template. Get started by adding the example mapping template to a new board, then take the following steps to make one of your own.
Understand the problem. Ask your product owner to define the user problem on a yellow sticky note, then explain how this translates to a need for a change in the product features. This helps the team better understand the problem.
Challenge the problem by asking follow-up questions. Collect all your team’s questions on red sticky notes, starting with “What if...?” These questions will live under your user story (the yellow sticky note).
Figure out the rules. Find the rules in the answers to the questions on red sticky notes. Each rule is your acceptance criteria for new product features. Make sure that every new rule can stand on its own. Ideally, it shouldn't be confused with or too similar to another rule.
Describe situations with relevant examples. Green sticky notes are where you record and collect interesting potential cases or instances. Keep the discussion going, and engage your team’s critical thinking skills by checking if you’ve reached the boundaries of the rule of your examples, as well as considering what happens if the rule fails.
Identify outcomes, impacts, and success metrics. What do you hope to accomplish with a new product feature, and how does it contribute to your business objectives? Consider how you might track and test the success of each proposed feature – what behavior you’ll be looking for and measuring.
Turn your stories into action items. These stories can be turned into a development plan for a new feature or product. They can also form the basis of a minimum amount of features needed to be valuable to your customer.
What is an example mapping technique?
The example mapping technique is a helpful method for creating detailed and specific user stories. By identifying examples, teams can delve into customer pain points and set criteria for new feature development. This technique was developed by Matt Wynne, who is the co-founder of Cucumber. It allows product managers and their teams to prioritize and refine product backlogs. Ideally, example maps promote shared understanding among cross-functional teams, such as product owners, testers, and developers, regarding the reasons for adding or changing product features. Through this collaborative approach, teams can define the expected user behavior across different scenarios. Effectively using an example mapping tool helps align cross-functional teams toward common objectives.
Get started with this template right now.
Agile Product Roadmap
Works best for:
Roadmap, Planning, Mapping
The Agile Product Roadmap template enables teams to visualize and communicate the strategic direction of their product development in an agile environment. It allows for flexibility and adaptation to changing requirements while providing a clear overview of priorities and timelines. By incorporating feedback loops and iterative planning, teams can ensure alignment with stakeholder expectations and deliver value incrementally.
Empathy Map by Pino de Francesco
Works best for:
Research & Design, Market Research
The Empathy Map template helps you understand your users' needs, behaviors, and experiences. By visualizing what users think, feel, see, hear, and do, you can gain deep insights into their motivations and pain points. This template is essential for creating user-centered designs and improving customer experiences.
Salesforce Implementation Plan
Works best for:
Roadmap, Planning, Mapping
The Salesforce Implementation Plan template offers a structured framework for planning and executing Salesforce deployment projects. By outlining key milestones, tasks, and dependencies, teams can ensure a smooth transition to the Salesforce platform. This template facilitates collaboration between IT and business teams, ensuring that implementation efforts are aligned with strategic objectives and deliver value to stakeholders.
Community Building: A 5 Step Roadmap
Works best for:
Roadmap, Planning, Mapping
Use this five step process for building a community development roadmap.
Weekly Planner by Elina Schäfer
Weekly Planner template is perfect for organizing your weekly tasks and schedules. It helps you prioritize activities, set deadlines, and manage your time effectively, ensuring you stay productive and on track throughout the week.
Competitor Product Research
Works best for:
Product Management, Planning
The Competitor Product Research template assists product teams in analyzing competitor offerings and market landscapes effectively. By identifying competitor strengths, weaknesses, and market trends, this template enables teams to uncover insights and opportunities for differentiation. With sections for conducting feature comparisons, SWOT analysis, and market positioning assessments, it facilitates informed decision-making and strategic planning. This template serves as a valuable resource for gaining competitive intelligence and driving product innovation and differentiation.