Event Storming
Workshop-based method to quickly find out what is happening in the domain of a software program.
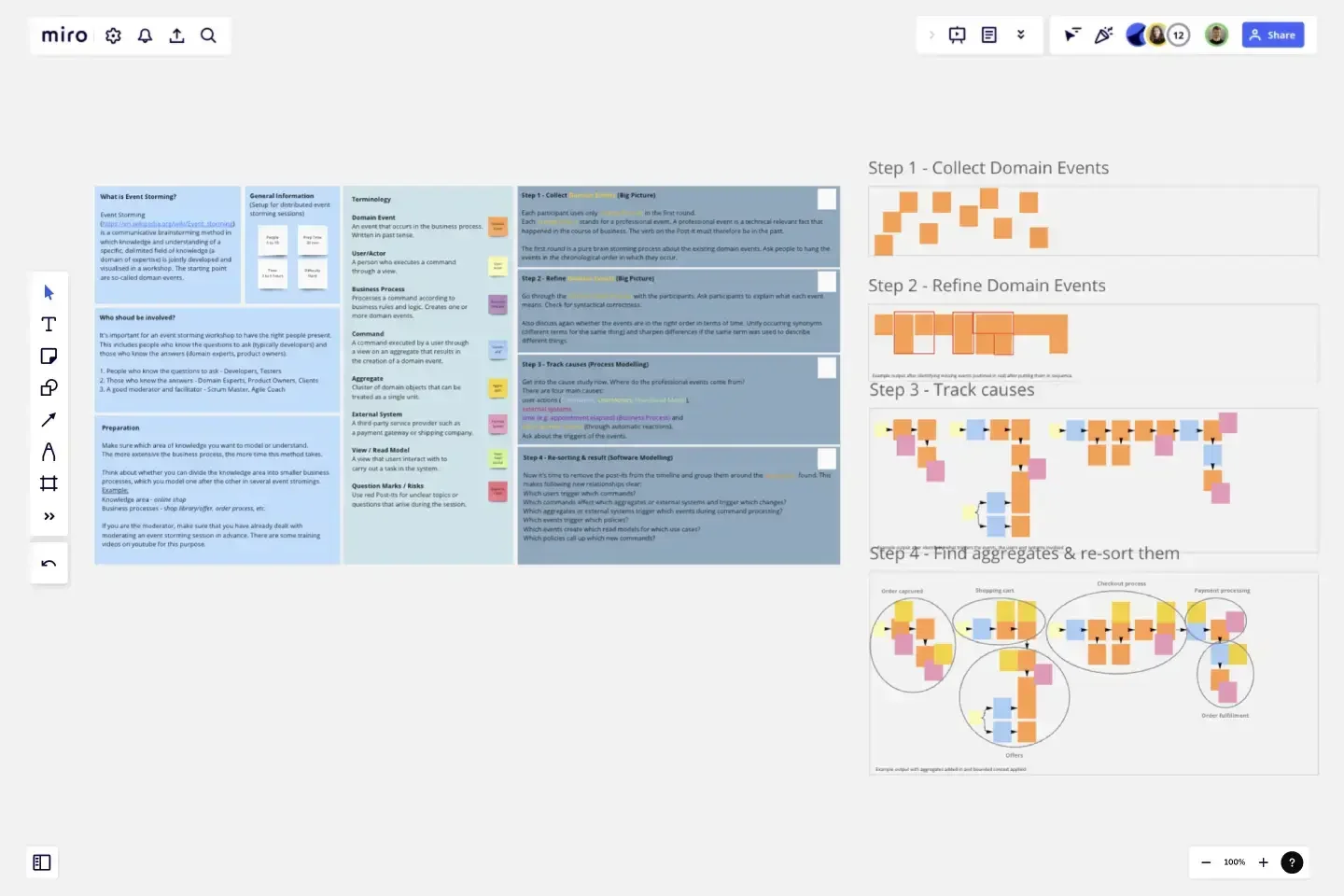
What is Event Storming?
Event Storming is a communicative brainstorming method in which knowledge and understanding of a specific, delimited field of knowledge (a domain of expertise) is jointly developed and visualised in a workshop. The starting point are so-called domain events.
The 4 evolution stages of Event Storming
Step 1: Collect Domain Events - discover them.
Step 2: Refine Domain Events - placing them in sequence.
Step 3: Track causes - modelling out the broader ecosystem.
Step 4: Re-sorting & result - categorize the events and build Bounded Contexts.
This template was created by Judith Birmoser.
Get started with this template right now.
Daily Stand-up Meeting Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Meetings, Software Development
The entire team meets to review the day before and discuss the day ahead. These daily meetings, also known as “scrums,” are brief but powerful — they identify roadblocks, give each team member a voice, foster collaboration, keep progress on track, and ultimately keep teams working together effectively. This template makes it so easy for you to plan daily standups for your sprint team. It all starts with picking a date and time, creating an agenda, and sticking with the same format throughout the sprint.
The 4-Step Retrospective
Works best for:
Retrospectives, Agile Methodology, Meetings
The 4-Step Retrospective template offers a simple yet effective framework for conducting retrospectives. It provides steps for reflecting on what went well, what didn't go well, what could be improved, and action planning. This template enables teams to systematically review past iterations, identify areas for growth, and implement actionable improvements. By promoting a structured approach to reflection and improvement, the 4-Step Retrospective empowers teams to drive continuous learning and enhancement effectively.
Project - Timeline & Key Infos
Works best for:
Agile, Project Management
The Project - Timeline & Key Infos template provides a visual framework for planning and tracking project timelines, milestones, and key information. It enables teams to align on project objectives, allocate resources, and monitor progress effectively. With customizable timelines and informative dashboards, this template empowers project managers and stakeholders to stay organized and informed throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring successful delivery within scope, time, and budget constraints.
Agile Transition Plan Template
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Agile Workflows
An Agile transformation roadmap can help you, your team, and your organization transition from rigid compliance-heavy methods to the more flexible Agile way of doing things incrementally. From requirements to integrations to security, you can map out your organization's moving parts as “swim lanes” that you can then update regularly. Use your roadmap as a way to tell the story of how you see your product growing over a period of time. Get buy-in without overselling and keep your roadmap simple, viable and measurable. By using an Agile transformation roadmap, you can avoid getting bogged down in details and instead invest in big-picture strategic thinking.
Hiring Process Template
Works best for:
Operations, Org Charts, Kanban Boards
Having a hiring process in place simplifies that process each step of the way, from recruiting for the position to making finalizing offers. This simple, effective template will give you a straightforward, high-level view of where employees are as they move from applicant to new hire.
Retrospective - Christmas Edition
Works best for:
Agile Methodology, Retrospectives, Meetings
The Retrospective Christmas Edition template offers a festive and themed approach to retrospectives, perfect for the holiday season. It provides elements for reflecting on the year's achievements, sharing gratitude, and setting intentions for the upcoming year. This template enables teams to celebrate successes, foster camaraderie, and align on goals amidst the holiday spirit. By promoting a joyful and reflective atmosphere, the Retrospective - Christmas Edition empowers teams to strengthen relationships, recharge spirits, and start the new year with renewed energy and focus effectively.