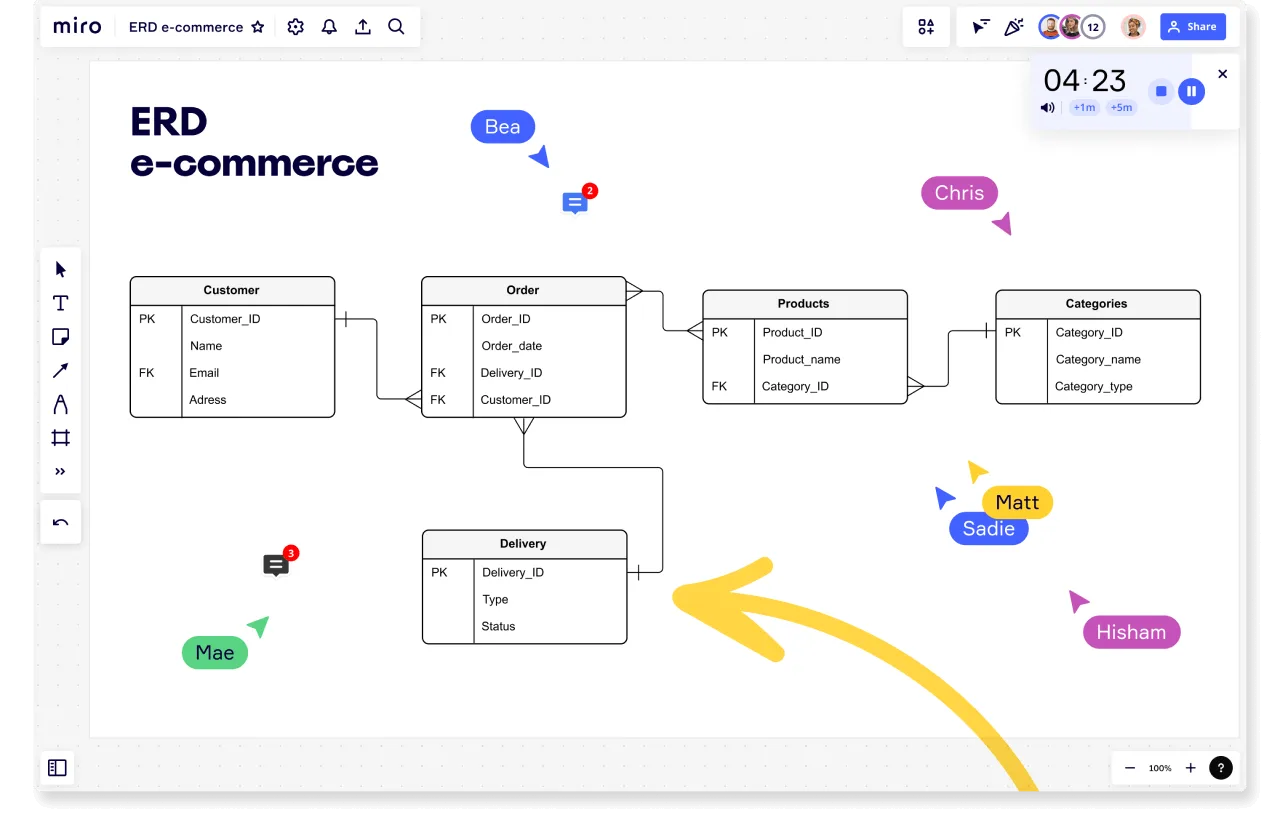
Crows Foot Notation

Understanding Crow's Foot notation
Entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs) are a fundamental tool in database design and business process modeling. Among the various notations used to create these diagrams, Crow's Foot notation stands out for its clarity and efficiency. This article delves into what Crow's Foot notation is, its symbols, and its practical applications, offering insights into why it's a preferred choice for professionals in these fields.
Crow's Foot notation, developed in the late 1970s, has evolved into a standard in ERD representation. Its name derives from the appearance of its symbols, which resemble a bird's foot.
What is Crow's Foot notation?
At its core, Crow's Foot Notation is a visual language used in ERDs to depict the relationships between entities in a database. It's known for its intuitive symbols that clearly represent the nature and cardinality of relationships.
Key symbols in Crow's Foot notation
Below you can see a brief description about the main symbols from crow's foot notation and they are commonly used:
Entities and attributes
Entity Sets: These are represented as rectangles and denote a collection of similar objects or concepts.
Attributes Types: Circles or ovals connected to entities, representing the data elements associated with each entity.
Relationships
Binary Relationships: Indicate associations between two entities.
Recursive Relationships: Show how an entity can be related to itself.
Cardinality and modality
One-to-One (1:1): A single entity instance of one type is associated with a single entity instance of another type.
One-to-Many (1:M): One entity instance is associated with multiple instances of another entity.
Many-to-Many (M:N): Multiple instances of one entity are associated with multiple instances of another.
Optional vs. Mandatory Relationships: Indicate whether an entity's participation in a relationship is optional or mandatory.
Advantages of using Crow's Foot notation
Clarity and Readability: Its graphical representation makes complex relationships easier to understand at a glance.
Industry Standard and Compatibility: Crow's Foot Notation is widely recognized and compatible with various database design tools.
Flexibility in Complex Diagrams: It effectively handles complex schemas without overwhelming the viewer.
Practical applications of crow's Foot notation
Crow's Foot Notation is a versatile tool with several practical applications across various domains. When use as a database design tool, it is extensively utilized for conceptualizing and structuring database schemas, making it an essential aspect of database architecture and management.
Its utility extends to business process modeling as well, where it plays a crucial role in mapping out organizational processes and their corresponding data requirements. Also, this clear and intuitive notation system is also highly valued in educational settings. It serves as an excellent resource for teaching concepts related to database and system design, helping students and professionals alike to grasp complex relational structures with greater ease.
Comparing Crow's Foot notation with other ERD notations
This notation can be confused with other famous ones, like UML and Chen's notation. Bellow you can see a few differences between the Crow's foot notation and others:
Chen's Notation: Focuses on using rectangles for entities and diamonds for relationships, emphasizing the roles played by entities in a relationship, which is different from Crow's Foot's approach of directly illustrating the nature and cardinality of relationships with specific line symbols.
IDEF1X Notation: Utilizes a more technical approach with rigid rules for depicting entities and relationships, including key-based identification, which contrasts with Crow's Foot's more intuitive and visually straightforward method of showing relationships and cardinalities.
UML Notation: Primarily used in software engineering, it incorporates a wider range of diagram types and focuses on object-oriented representation, differing from Crow's Foot which is more specialized for database schema representation with a focus on entity relationships and cardinalities.
Conclusion
Crow's Foot Notation remains a vital tool in the world of database and system design. Its ability to simplify complex relationships and enhance readability makes it indispensable for professionals and educators alike.